Analyses

The European Union and its crises
Since the Amsterdam Treaty of 1999, various crises have served as a pretext for expanding EU security structures and the powers of repressive authorities. Politically motivated human rights abuses remain the order of the day and have been exacerbated by the recent “migration crisis” at the EU's eastern borders.

Submission for the EU Rule of Law Report 2023
On 20 January, we filed a submission to the European Commission's public consultation for its Rule of Law Report 2023, which will cover developments in 2022. Our submission highlights a number of topics - in particular regarding rule of law issues at EU level, surveillance, access to an effective remedy and the criminalisation of the press - that have not received sufficient attention in previous iterations of the report.

Frontex and deportations, 2006-21
Data covering 16 years of Frontex’s deportation operations shows the expanding role of the agency. We have produced a series of data visualisations to show the number of people deported in Frontex-coordinated operations, the member states involved, the destination states, and the costs.

Evaluation of the 2019 Frontex Regulation: Statewatch submission to the European Commission call for evidence
We made a brief submission to the European Commission's call for evidence to inform the evaluation of the 2019 Frontex Regulation. The evaluation is due to be carried out between December 2022 and October 2023 by an external consultant. Our submission highlights issues concerning fundamental rights, transparency and accountability.

The Melilla border deaths represent a new phase in the bloody story of Fortress Europe
On 24 June dozens of people died after attempting to cross the heavily-fortified border from Morocco into the Spanish enclave of Melilla. A report by the Nador branch of the Association Marocain des Droits Humains (AMDH), summarised and built upon here, examines the build-up to and immediate aftermath of the deadly incident. The report documents multiple human rights violations and also reveals a significant shift: from EU authorities undertaking pushbacks and leaving people to their fate in situations in which they may come to harm, to EU authorities undertaking pushbacks with the explicit knowledge that they would be beaten and treated in an inhumane and degrading manner by their non-EU ‘partners’.

Questioning the interviewers: Frontex’s covert interrogations at the Spanish southern border
Tony, a police officer deployed multiple times in Frontex operations in Spain and Greece, slips on the word “interrogate”. He immediately corrects himself: “We are not allowed to say interrogate”. We both know that the term interrogation fits perfectly well.

Tunisian deportees in Italy denied rights under European “migration management” policies that seek to exclude
On 28 November 2021, Wissem Ben Abdellatif, a 26-year-old Tunisian man, died in a hospital in Rome after suffering a heart attack. He had been transferred to the hospital from the Ponte Galeria detention centre, where he was being held whilst awaiting deportation. A new report dedicated to his memory examines the experiences of Tunisian citizens deported from Italy. Based on over 50 in-depth interviews with deportees, it concludes that Tunisians are regularly denied their rights after arriving in Italian territory (for example, to legal advice, information, or adequate living conditions), and that the situation is propelled by a security-minded approach to migration that has been implemented across the EU and its member states for at least two decades.

Frontex: more power, no responsibility? Mega-agency lacks real accountability structure
Since 2004, four successive regulations have increased the agency’s resources and mandate, but no adequate control mechanisms have followed to balance these with legal or political accountability.

Building walls, restricting rights: Lithuania's response to the EU-Belarus border 'crisis'
After the ongoing politico-diplomatic clash between the EU and Belarus reached a peak in the summer of 2021, press attention turned towards the situation at the Polish-Belarussian border, where thousands of people arrived hoping to travel onwards to EU territory. However, the response from the Lithuanian authorities also merits examination: the country's efforts to prevent irregular arrivals have been widely supported by the EU, despite widespread allegations of fundamental rights violations.
Funds for Fortress Europe: spending by Frontex and eu-LISA
In the wake of the so-called “refugee crisis” of 2015, EU governments took the opportunity to reinforce the powers and mandates of EU agencies concerned with immigration and border control. Expanded legal remits were accompanied by vast increases in expenditure. But where has that money gone and what has it been used for?

Frontex: the ongoing failure to implement human rights safeguards
A legal case alleging that Frontex was involved in an illegal deportation and the annual report of its Consultative Forum on Fundamental Rights, made up of NGOs and international organisations, show once again that fundamental rights are not at the top of the agency’s agenda.

Série Frontex : résumés
Depuis le lancement de ses opérations conjointes, Frontex a été accusée de détourner le regard de ses obligations légales en matière de respects des droits, et en particulier concernant le sauvetage en mer. Statewatch, membre de Migreurop, à travers la plume de Jane Kilpatrick, chercheur et membre de l’équipe salariée de Statewatch, et Marie Martin, collaboratrice de Statewatch, a publié une série de trois analyses sur les aspects juridiques et politiques qui ont amené à cette situation « d’impunité choisie ». Vous trouverez ci-joint un résumé en anglais et français, ou qui souhaitent accéder aux arguments principaux émis dans ces analyses. (Versions anglaises ci-dessous).

UK: Statewatch submission to consultation on reform of the Data Protection Act 2018
Submission by Statewatch to the Department of Culture, Media and Sport’s consultation on reforms to the UK’s Data Protection Act 2018.
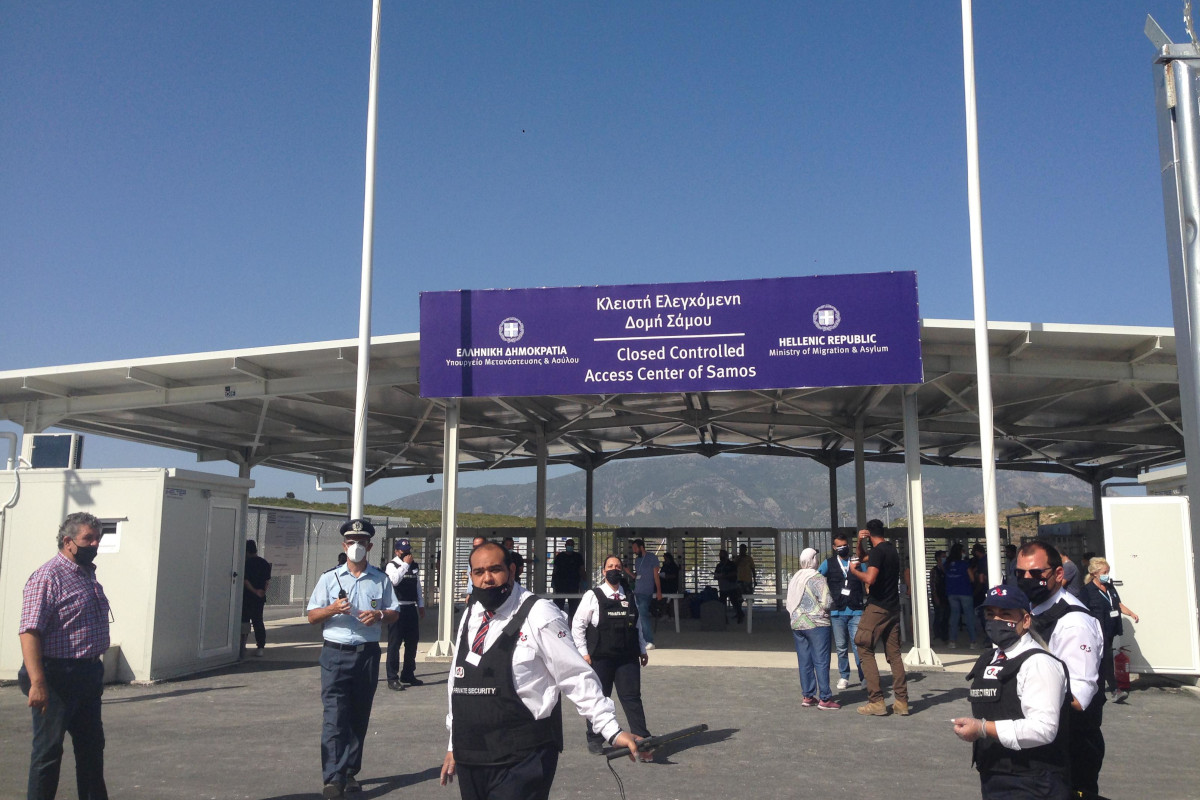

Greece: The new hotspots and the prevention of “primary flows”: a human rights disaster
The Greek government and the EU have evicted various self-managed hospitality structures and are now closing down the squalid, state-run refugee camps on the islands of the Aegean. People are being transferred to newly-built "closed controlled access centres". These prison-like facilities, which are coming into use at the same time as a the services available to refugees are being cut back, are having injurious effects upon people's mental health and wellbeing. Nevertheless, with the Greek government focusing on preventing "primary flows", it seems the new camps are set to play a growing role in the detention of people awaiting deportation.

Frontex cooperation with third countries: examining the human rights implications
While Frontex is currently under unprecedented examination for human rights violations at the EU’s borders, its work beyond EU borders remains barely scrutinised, write Dr Mariana Gkliati and Statewatch researcher Jane Kilpatrick in Forced Migration Review.

UK: Nationality and Borders Bill: Biometric 'permission to travel' scheme will affect tens of millions of people
Submission by Statewatch to the UK Parliament Joint Committee on Human Rights inquiry into the human rights implications of the Nationality and Borders Bill.

Frontex, secrecy and story-telling: control of information as super-strategy
EU border agency Frontex spends a significant amount of time and money on its public image, and insists that its activities are fully transparent. However, that public image is - unsurprisingly - heavy on spin, and panders to far-right narratives. Meanwhile, its commitment to transparency is questionable - to say the least.

To SAR or not to SAR, part 2: Legal firewalls of a very political agency
The second part of an analysis looking at the legal firewalls that create blurred responsibilities in cases of search and rescue and pushbacks, shielding EU border agency Frontex from accountability measures.

To SAR or not to SAR, part 1: Why is Frontex expected to save lives at sea?
The first in a four-part series looking into the activities and operations of EU border agency Frontex, examining the evolution of the agency’s search and rescue obligations since it was founded in 2004. Many organisations have warned that “protecting borders” may conflict with “protecting lives” and experience suggests that, what are presented as two distinct objectives are, more often than not, part of conflicting policy agendas. The controversial and deadly practices that have been brought into the spotlight by the Aegean allegations are ultimately the result of political decisions that highlight the dubious priorities of the EU, its member states and its agents – Frontex included.
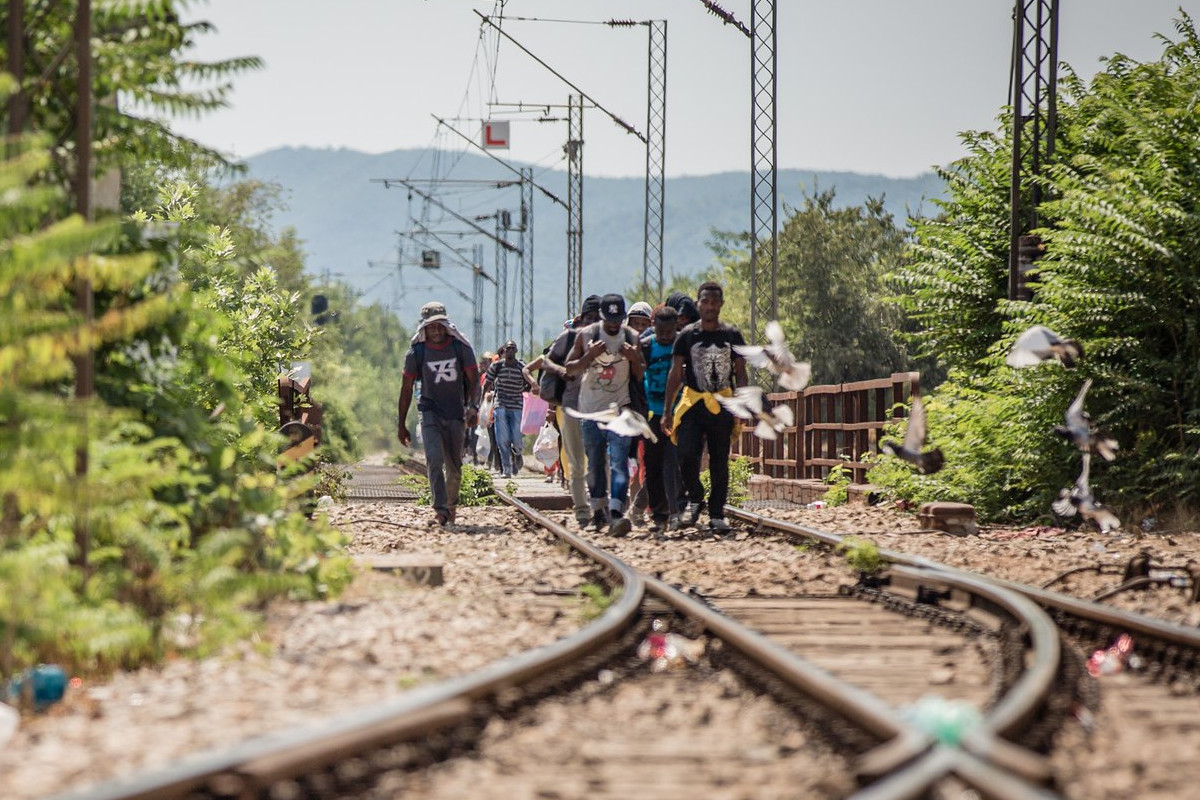

Foreign agents and violence against migrants at the Greek-Macedonian border
An increasing number of reports of violent pushbacks at the Greek-Macedonian border have been collected by volunteers in recent years. Some reports allege the presence of Frontex, but bilateral policing deals in place may also explain the presence of foreign officers in Macedonia. The violence underpins a long-standing plan to close the ‘Balkan Route’ and keep people out of ‘core’ EU territory. Whoever is behind the violence, there is no shortage of border guards to mete it out – but justice is in short supply.
Spotted an error? If you've spotted a problem with this page, just click once to let us know.