News
Launched in 1999 and updated regularly, Statewatch News includes our own reporting and writing as well as articles, announcements, documents and analyses from elsewhere on civil liberties, EU policies and state practices. You can receive updates in your inbox by signing up to our mailing list, or use our RSS feed to get instant alerts.

EU planning new anti-migration deals with Egypt and Tunisia, unrepentant in support for Libya
The European Commission wants to agree “new anti-smuggling operational partnerships” with Tunisia and Egypt before the end of the year, despite longstanding reports of abuse against migrants and refugees in Egypt and recent racist violence endorsed by the Tunisian state. Material and financial support is already being stepped up to the two North African countries, along with support for Libya.
USA seeks bilateral deals for access to European “criminal, terrorist, and identity records”
The USA’s proposed Enhanced Border Security Partnerships would entail “systematic and continuous” exchanges of sensitive personal data between participating states. The European Commission has indicated that its working group with the USA has stopped operating, and that plans are instead being negotiated bilaterally between member states and the USA.
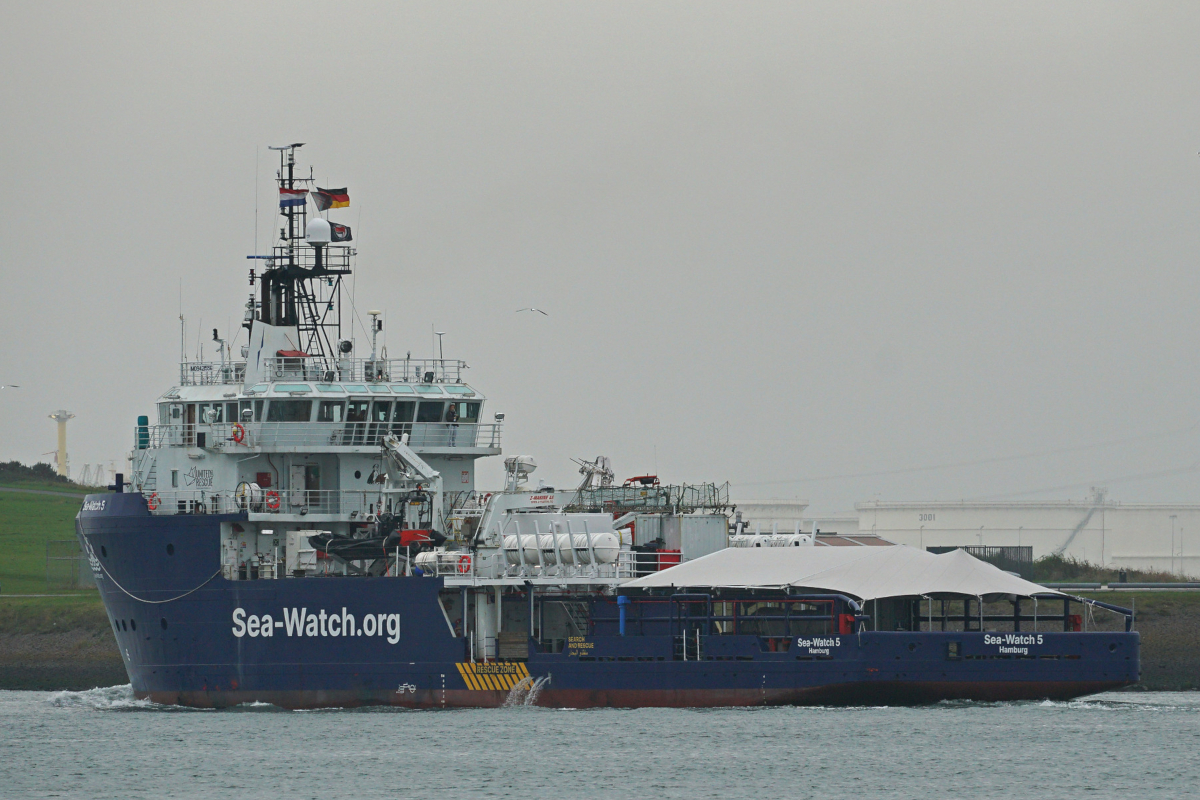

EU mulls intelligence-gathering obligations for search and rescue operations
Draft European Commission proposals would impose intelligence-gathering requirements on any ships that engage in search and rescue (SAR) operations at sea, in the name of "addressing the needs of those onboard as well as facilitating a smooth disembarkation and first reception". An employee of a search and rescue organisation has warned that "civil assets used in sea rescue operations should not be tasked with any law enforcement duty."

Campaign celebrates success as three English universities divest from the border industry
Three English universities have divested from companies profiting from border violence in a major win for the Divest Borders campaign. However, over £300 million of university endowments still remain invested in the border industry.

UK participation in “unnecessary” police facial recognition system needs “open, thorough, democratic debate”
MPs must ensure thorough scrutiny and a meaningful democratic debate on potential UK participation in a pan-European police facial recognition system that is unnecessary, disproportionate and undesirable, says a statement coordinated by Statewatch and signed by 13 other civil society organisations.
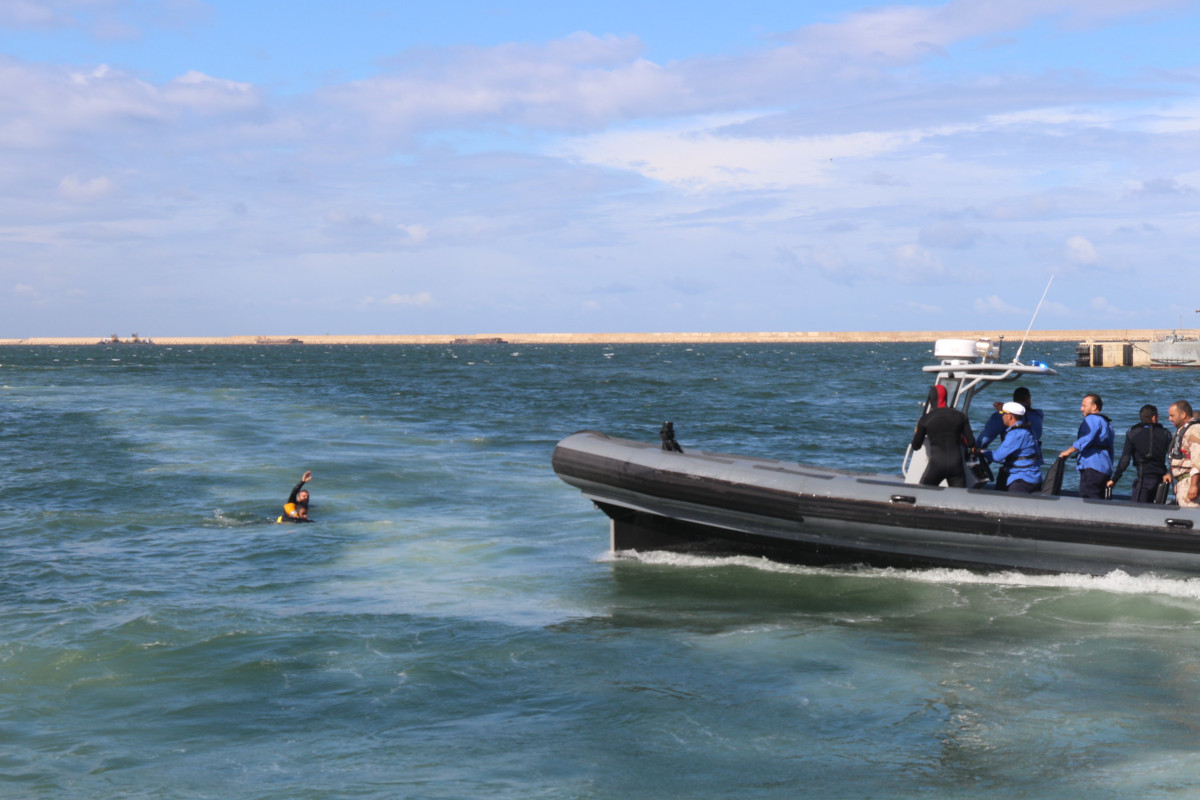

EU to step up support for human rights abuses in North Africa
In a letter to the European Council trumpeting the EU’s efforts to control migration, European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen highlighted the provision of vessels and support to coast guards in Libya and Tunisia, where refugee and migrant rights are routinely violated.

EU: More surveillance, funding and operational cooperation to fight migrant smuggling
A Spanish presidency note to member state representatives in the Council identifies cross-border organised crime as a key threat to the correct functioning of the Schengen area, calling for additional impetus in 2023-2024 to fight “cross-border, serious and organised crime”. Crimes involving smuggling and exploitation (including of children, trafficking, sexual exploitation) are deemed challenges for external border management and the Schengen area.

Database delays: new timetable for interoperable EU policing and migration systems by 2027
EU interior ministers have agreed another revised timeline for the plan to make all justice and home affairs databases "interoperable", with the aim now to have the systems up and running by 2027. Mandatory biometric border checks may now be introduced progressively, in the hope of limiting delays at border crossing points.

Spanish Presidency: more funds needed for border externalisation if EU is to stay "credible vis-à-vis key third countries"
Externalisation of migration control is back on the agenda of the Justice and Home Affairs Council today. The Spanish Presidency's recent proposal for a "preventive" approach is to be debated further, with discussion focusing on ways to "optimise" the EU's current "toolbox" for externalisating migration controls and how to ensure "robust, efficient and coordinated financial support," including direct funding to third countries so that the EU can remain "credible".

UK government’s disrespect for rights could jeopardise cooperation with EU, warn MEPs
The UK government’s intention to undermine human rights and wipe swathes of retained EU legislation off the books has set alarm bells ringing in the European Parliament’s civil liberties committee, which approved an opinion last week expressing “deep concern over current legislative processes in the UK.”

EU seeking informal agreement to boost deportations to Iraq
The EU is pushing for a “non-binding instrument” with Iraq in order “to increase Iraq’s cooperation on readmission” – that is, acceptance of deportations.

Spanish Presidency’s call for “a preventive model” for migration: more of the same
A discussion paper circulated on 26 September by the Spanish Presidency proposes a switch in the external dimension of migration from “a reactive to a preventive model”. In reality it appears that this is little more than doubling down on existing plans. The paper was circulated to inform discussion at the Justice and Home Affairs Council meeting last week.

EU gears up for renewed crackdown on migrant smuggling
At the Schengen Council meeting on 19 October, ministers will discuss how to ramp up the EU's repressive measures against migrant smuggling and decide on "actions, commitments and sustainable solutions." A draft paper from the Spanish Council Presidency gives an indication of the plans that are in the works.

Frontex: deportations at record high in first half of 2023
The European Union's border agency, Frontex, facilitated the deportation of nearly 18,000 individuals from EU territory during the first half of 2023, marking an unprecedented peak. This surge in removals, executed through both scheduled flights and "voluntary" return procedures, demonstrates a 60% upswing in deportations compared to the corresponding period in 2022.

Tracking the Pact: Derogations all round in Council's latest crisis Regulation edit
Of the five legislative proposals in the EU's Pact on Migration and Asylum, there is only one for which the Council has not so far adopted a negotiating position: the crisis and force majeure Regulation. The main purpose of the law is to set out derogations from other measures in the Pact, which are all due to be approved by next spring. The latest version of the text (published here) was up for discussion yesterday at the Justice and Home Affairs Council, which failed to reach agreement on it. Another attempt will reportedly be made on Monday.

After the Niger coup, Spanish Council Presidency asks: "How can we continue cooperation on migration and border management?"
Earlier this month, an article published by Statewatch questioned how long it would be before the EU's cooperation on security and migration with Niger - which was halted after the coup at the end of July - was restarted. A document circulated by the Spanish Presidency of the Council on 8 September suggests that, despite the EU condemning the coup "in the strongest terms," there is enthusiasm to get joint projects going again.

Civil society calls on legislators to ensure the AI Act upholds the rule of law
In another warning on the dangers posed by the EU's Artificial Intelligence Act, more than 60 organisations (including Statewatch) are calling on EU legislators to ensure that the text upholds the rule of law. An open letter calls: for fundamental rights impact assessments for all high-risk AI systems; to ensure that systems used for national security purposes fall under the Act; and to ensure that AI developers cannot exempt themselves from the Act. "As the EU navigates the complexities of the digital age, it is of the utmost importance that we do not lose sight of our core values," says the letter.

Global call to stop facial recognition surveillance
Facial recognition and other forms of biometric surveillance pose huge dangers for rights and freedoms in public space. They make it possible for pervasive tracking of individuals' movements and activities; are used to infer or monitor emotions and alleged "suspicious behaviours"; and have been responsible for wrongful arrests and convictions, and the suppression of protests. The dangers they pose are so significant that a coalition of more than 110 civil society organisations (including Statewatch) and 60 eminent individuals are making a simple demand to governments: stop using facial recognition for the surveillance of publicly-accessible spaces and for the surveillance of people in migration or asylum contexts.

Interpol: multi-million dollar “predictive analytics” system under construction
The International Criminal Police Organisation, Interpol, is building a vast data-processing platform called INSIGHT that is ultimately supposed to provide police forces around the globe with “predictive analytics” generated from Interpol’s internal data, information received from its member states, “external” sources such as commercial databases, and “visual, video, audio recognition, facial and bio-data matching.” The US State Department has so far committed more than $12 million for the project.

Police AI needs strict limits and controls, warn civil society organisations
Secret "trilogue" negotiations on the EU's proposed Artificial Intelligence Act are ongoing, and next week MEPs and EU member state representatives will start discussing bans and prohibitions. The week after, decisions are expected on whether to classify the use of AI for migration and security purposes as "high risk" or not. A statement directed at decision-makers and signed by 115 associations and individuals, including Statewatch, calls for strict limits and controls in the AI Act "to prevent harm, protect people from rights violations and provide legal boundaries for authorities to use AI within the confines of the rule of law."
Spotted an error? If you've spotted a problem with this page, just click once to let us know.